+86 183 6377 3366
+86 183 6377 3366 Main process of glass bottle production process Glass bottle production raw materials and processes
1. Main process of Glass Bottle production process
The production process of glass includes: ingredients, melting, forming, annealing and other processes. It is introduced as follows:
1. Ingredients, weigh various raw materials according to the designed material square sheet, and mix them evenly in a mixer. The main raw materials of glass include: quartz sand, limestone, feldspar, soda ash, boric acid, etc.
2. Melting, heating the prepared raw materials at high temperature to form uniform bubble-free glass liquid. This is a very complex physical and chemical reaction process. The melting of glass is carried out in the melting kiln. There are two main types of melting kilns: one is a crucible kiln, where the glass frit is contained in the crucible and heated outside the crucible. The small crucible kiln only has one crucible, and the larger one can reach 20 crucibles. The crucible kiln is produced intermittently. Now only optical glass and color glass are produced in crucible kilns. The other is a pool kiln, where the glass frit is melted in the kiln pool and the open flame is heated on the upper part of the glass liquid surface. The melting temperature of glass is mostly between 1300 and 1600゜C. Most of them are heated by flame, and there are also a small amount of electric current, which is called an electric melting kiln. Now, pool kilns are produced continuously. Small pool kilns can be several meters, and large ones can be as large as more than 400 meters.
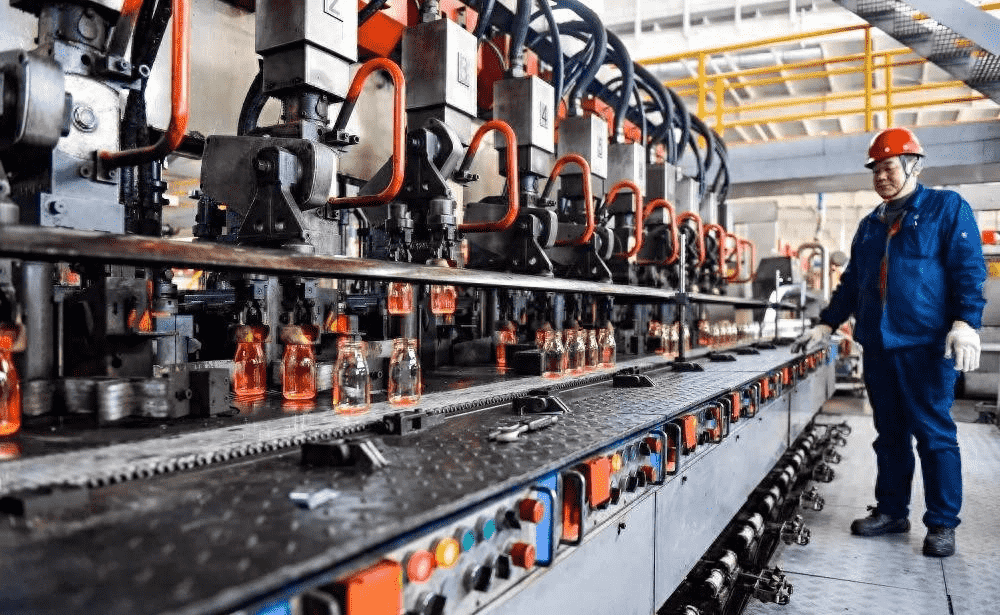
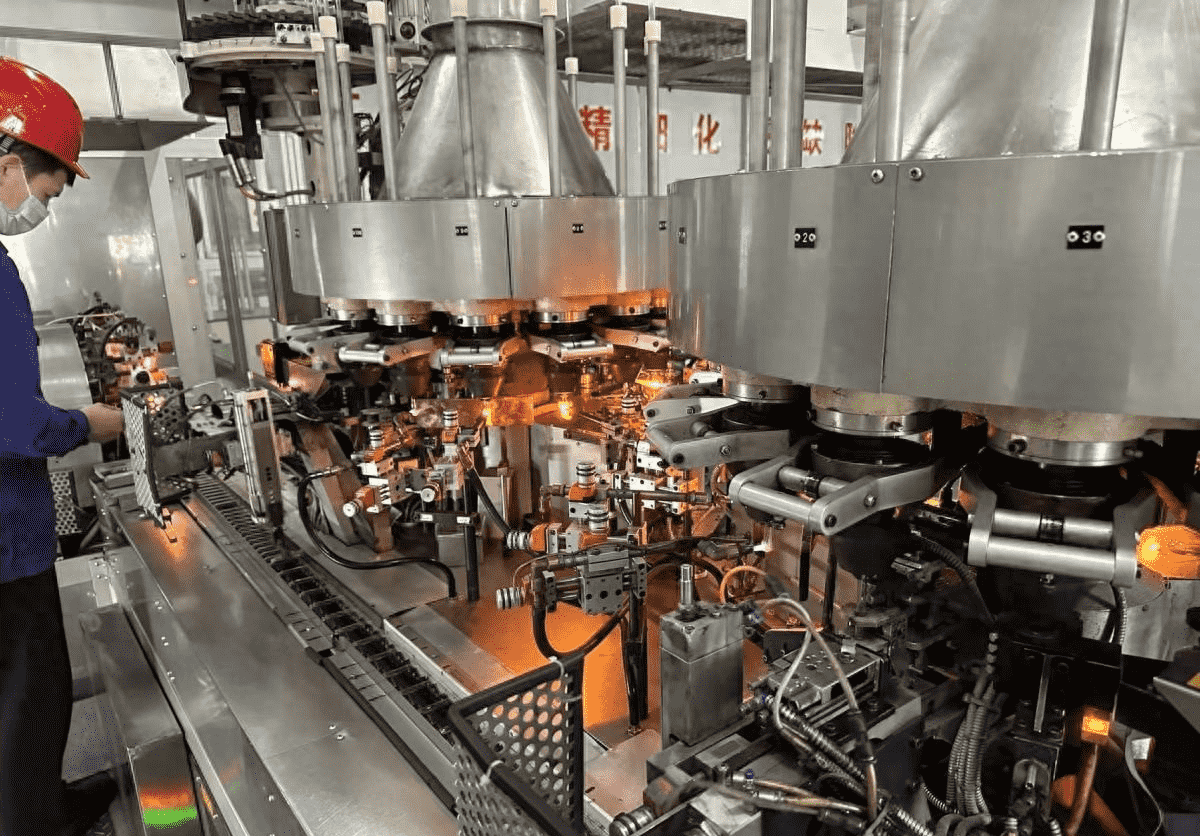
3. Forming means converting the melted glass liquid into a solid product with a fixed shape. Forming must be within a certain temperature range. This is a cooling process. The glass first changes from viscous liquid to plastic, and then turns into a brittle solid. The forming method can be divided into two categories: artificial forming and mechanical forming.
A. Manual forming. There is also (1) blowing, using a nickel-chromium alloy blowing pipe, picking a ball of glass in the mold while turning and blowing. It is mainly used to form glass bubbles, bottles, balls (for scratching glasses). (2) Pulling, after blowing into small bubbles, another worker sticks it with a top plate, and the two of them pull it while blowing and pulling it is mainly used to make glass tubes or rods. (3) Pressing, picking a ball of glass, cutting it with scissors to make it fall into the mold, and then pressing it with a punch. It is mainly used to form cups, plates, etc. (4) Free forming, after picking up the material, use pliers, scissors, tweezers and other tools to directly make handicrafts.
B. Mechanical forming. Because manual forming has high labor intensity, high temperature and poor conditions, most of them have been replaced by mechanical forming except for free forming. In addition to pressing, blowing and drawing, mechanical forming also has (1) calendering method, which is used to produce thick flat glass, engraved glass, wire-clad glass, etc. (2) casting method, which produces optical glass. (3) centrifugal casting method, which is used to make large-diameter glass tubes, utensils and large-capacity reaction pots. This is to inject glass melt into a high-speed rotating mold, and the glass is tightly attached to the mold due to centrifugal force. On the wall, rotate and continue until the glass hardens. (4) Sintering method is used to produce foam glass. It is to add foaming agent to the glass powder and heat it in a covered metal mold. The glass forms many closed-mouth bubbles during the heating process. This is a good insulation and sound insulation material. In addition, the forming of flat glass includes vertical guide method, flat drawing method and float method. The float method is a method to let the glass flow float on the surface of molten metal (tin) to form flat glass. Its main advantages are the high quality of the glass (flat and smooth), fast pulling speed, and large output.
4. Annealing, the glass undergoes intense temperature changes and shape changes during the forming process, which leaves thermal stress in the glass. This thermal stress will reduce the strength and thermal stability of the glass products. If it is cooled directly, it is likely to burst on its own during the cooling process or later storage, transportation and use (commonly known as the cold explosion of glass). In order to clean up the cold explosion, the glass products must be annealed after forming. Annealing means insulation or slow cooling within a certain temperature range for a period of time to clean or reduce the thermal stress in the glass to the allowable value.
In addition, in order to increase their strength, some glass products can be rigidized. They include: physical rigidization (quenching), used for thicker glass cups, desktop glass, automobile windshield, etc.; and chemical rigidization (ion exchange), used for watch masking glass, aviation glass, etc. The principle of rigidization is to generate compressive stress on the surface layer of the glass to increase its strength.
2. Raw materials and processes for glass bottle production

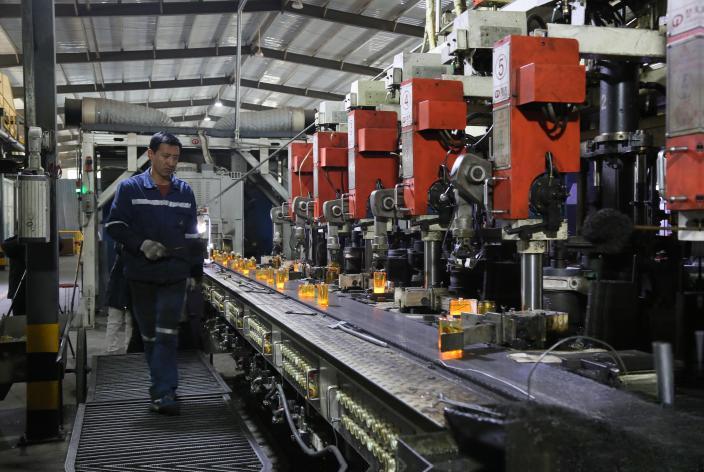
1: Raw materials (there are roughly 7-12 types of raw materials and 4-6 types of main materials) are melted at high temperature by the kiln, and dripped into the mold of the production equipment (the main production equipment includes ranks, artificial mouth machines, artificial mouth pourers, cup presses, etc.), and are made through blowing and pressing processes, and then annealed and cooled by the annealing furnace.
2: ① Crush the block raw materials to dry the damp raw materials, and remove the iron-containing raw materials. ② Prepare the compound material. ③ Heat the glass compound material at high temperature (1550~1600 degrees) to become liquid glass. ④ Forming. Put the liquid glass into the mold to make glass products of the required shape. ⑤ Heat treatment.
3: Main raw materials: quartz sand, limestone, feldstone
Production technology: ① Preprocessing of raw materials. Crush the block raw materials to dry the wet raw materials, and remove the iron-containing raw materials to ensure the quality of the glass. ② Preparation of compound materials. ③ Melting. Glass compound materials are heated at high temperature in a pool kiln or crucible kiln to form liquid glass that is uniform, bubble-free and meets the molding requirements. ④ Forming. Process the liquid glass into products of the required shape, such as flat plates, various vessels, etc. ⑤ Heat treatment. Through annealing, quenching and other processes, stress, phase separation or crystallization inside the glass, and change the structural state of the glass.